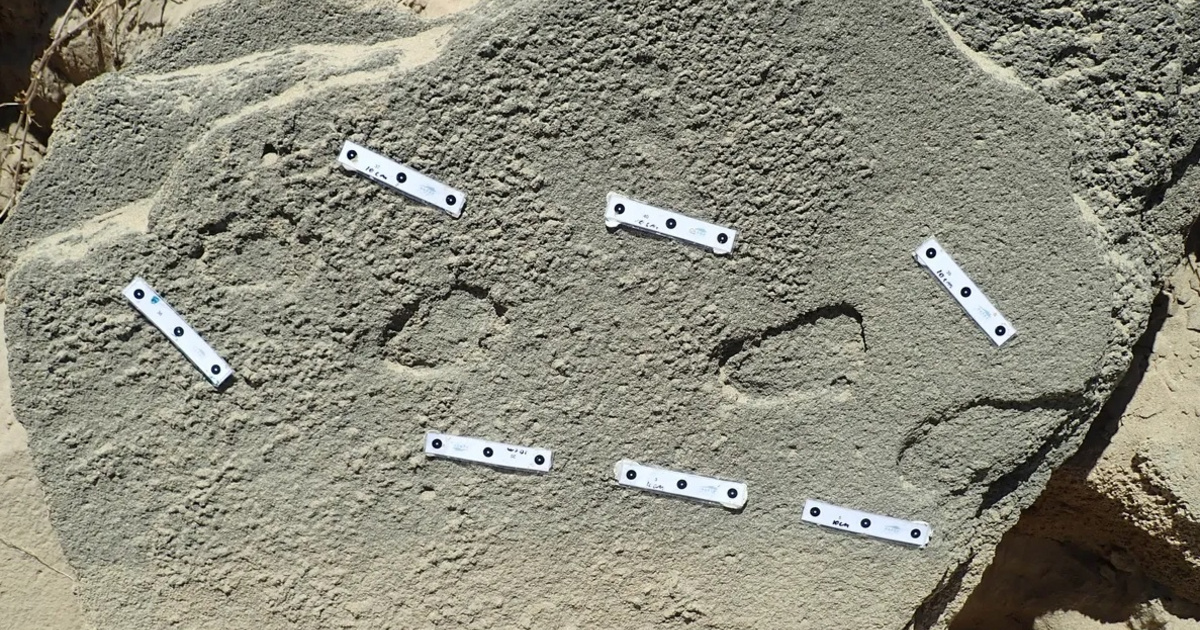
Based on the analysis of South African researchers, the tracks discovered around the coast of Cape Town may be the first known evidence of human shoes. There are no toes visible on the surviving Paleolithic prints, but their features are sharp, and some of the details appear to be the attachment points of the leather straps attached to the sole.
the Ikonos According to a study published in the Nelson Mandela University Journal, researchers identified three different locations. The ruins found at the site called Kleinkrantz have been found between 79,000 and 148,000 years ago. The Jokama site is estimated to be between 73,000 and 136,000 years old. A third similar fossil footprint was found at the Cape Woody site in Addo Elephant National Park. The age of the ruins cannot be estimated directly, but only based on sediments and other rocks found in the surrounding areas.
In all cases, the traces point to hominins. Depending on their size, they may be left out by children or young adults
– said the researchers.
To prove their theory, the experts tested the hard-soled sandals of local San residents borrowed from the museum—these left sharply defined marks in the sand. According to the researchers, this is indirect evidence, but in their opinion, sandals played a very important role in the coastal lifestyle: in this environment, not only sharp rocks are an annoying hindrance, but also anyone who has stepped on a sea urchin, because, for example, they can You get seriously injured.
In prehistoric times, a serious leg wound could be fatal
– They shed light.
Photo: Charles Helm
Of course, no sandals could have survived from this era. So the oldest remaining shoe is a 9,000-year-old braided sandal made of sage, found in Oregon, under a layer of volcanic ash. 5,500-year-old shoes have also been found in Israel and Armenia, and a pair of surranos has been found in Autzen, which was frozen 5,000 years ago in the South Tyrolean Alps.
The oldest known footprints were found in a cave in Greece, probably left there by Neanderthal children 130,000 years ago. Similar antiquities have also been found in France, but their probative value – in both cases – is in dispute. As the South African researchers cautioned in their article, they tried to approach the issue with caution and refrained from raising the discovery. And remember the case in which a human shoe print was found in Nevada in 1880, and it was later found to be a giant sloth’s footprint.