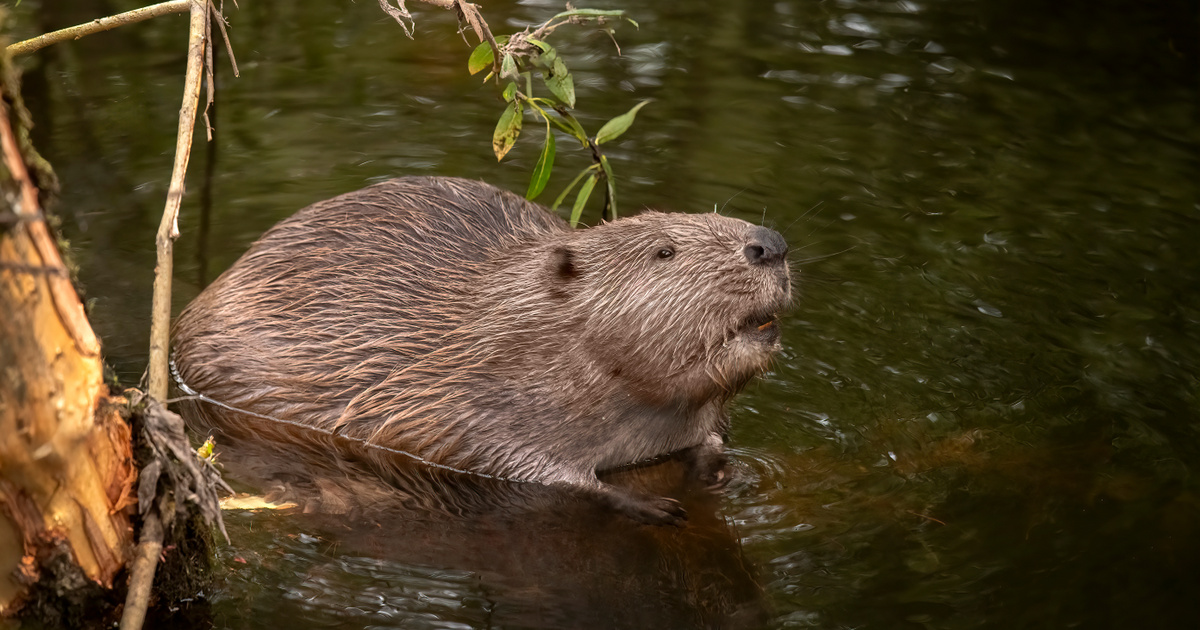
In North America, the animal has been exterminated for decades because farmers and logging companies found it harmful, and other hunters killed the beneficial animal for its fur. Because yes, their beneficial dam-building work is vital to the ecosystem, helping to irrigate drier soils, and their dams can also protect other species, and they've begun to realize this recently. Its work can help not only regulate water, but also keep fires under control, so the beaver can be nature's firefighter. Question: Isn't it too late to rehabilitate beavers?
The beaver has done almost everything in vain to protect the environment extinct From US territory: poison, traps, dam bursting – everything was used against it, with such success that the number of its copies, between 100 and 200 million, had shrunk to about 100,000 by the twentieth century.
It's the beaver's turn
In Oregon, beavers have been considered predators for 70 years, and here, according to the law, predators can be killed without a second thought. But last year, the bill nicknamed the “Safe Beaver” was finally passed, under which the animal is no longer a predator and its life cannot be taken without a permit. The proposal emphasizes the important ecological role of the animal, calling it nature's engineer, which can also help other species survive.
But the farmers did not welcome the bill with great joy. The vice president of an agriculture advocacy organization said the new bill is too complicated and doesn't even reflect the value beavers have in the ecosystem or the benefits they bring to floodplain restoration.
Beaver pelt hunting began in the late 1600s and was widespread in North America for two centuries, but logging companies continued to kill beavers even after demand for their pelts declined. Lumber supply companies were alarmed by the abundance of beavers and accused the rodents of chewing their products, although beavers are selective and do not buy all the lumber.
Indian symbol
Kenneth McDarmint, a member of the Tule River Indian Tribe in California, has been fighting to reintroduce beavers for years. In 2020, he applied for a grant to the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service to restore beavers and grasslands. It was successful, and in 2022 the development of a comprehensive, financially supported beaver management plan began.
The Klamath Tribe in Oregon took matters into their own hands to deal with the beaver problem: they formed a river restoration team to deal with the missing beavers, built beaver dams on several streams to trap sediment, and improved the condition of degraded riverbeds. This will revive coastal plants that will be a food source for returning beavers.
Beavers are not only other animals (otters, turtles, fish) Environments They support the landscape but also effectively protect it from wildfires, by creating lakes with dams and then digging a long canal, which can spread water even in the driest landscape. With the slow flow of water, the soil can absorb moisture, which helps plant life, but it also prevents fires by keeping the ground moist.
Hungarian beavers
The case of the beaver at home was reported to ELTE researchers last year Stady the Preserving biological diversity In the specialized magazine. The Eurasian beaver became extinct in Hungary in the mid-19th century, and its return was due to spontaneous colonization and beaver reintroduction campaigns (1996-2008) that began in the early 1990s. In 2016, the population was estimated at 4,000-5,000 individuals.
The study describes how beavers can modify the original shoreline by building dams and creating extensive wetlands, depending on the landscape. Beaver dams can improve groundwater levels and create new willow planting sites. But the truth is that their intense chewing can endanger some plant species, especially native softwoods. The animal is generally herbivorous, but its favorites are willow and aspen, which it searches for right at the water's edge, especially if their trunk is 5-9 cm in diameter. This is the preferred thickness for consumption. However, due to overconsumption, the survival and regrowth of these trees must be consciously supported, for example by increasing the groundwater level and improving hydrological conditions.