Galaxies can exist in fairly limited forms because the universe has not given them much freedom. Therefore, they are usually regular, i.e. they can be spiral, elliptical, polygonal or irregular. However, these objects are the rare exception.
These talking spiral galaxies are a major component of the modern universe, but a study by astronomers using the Hubble Space Telescope recently challenged that view.
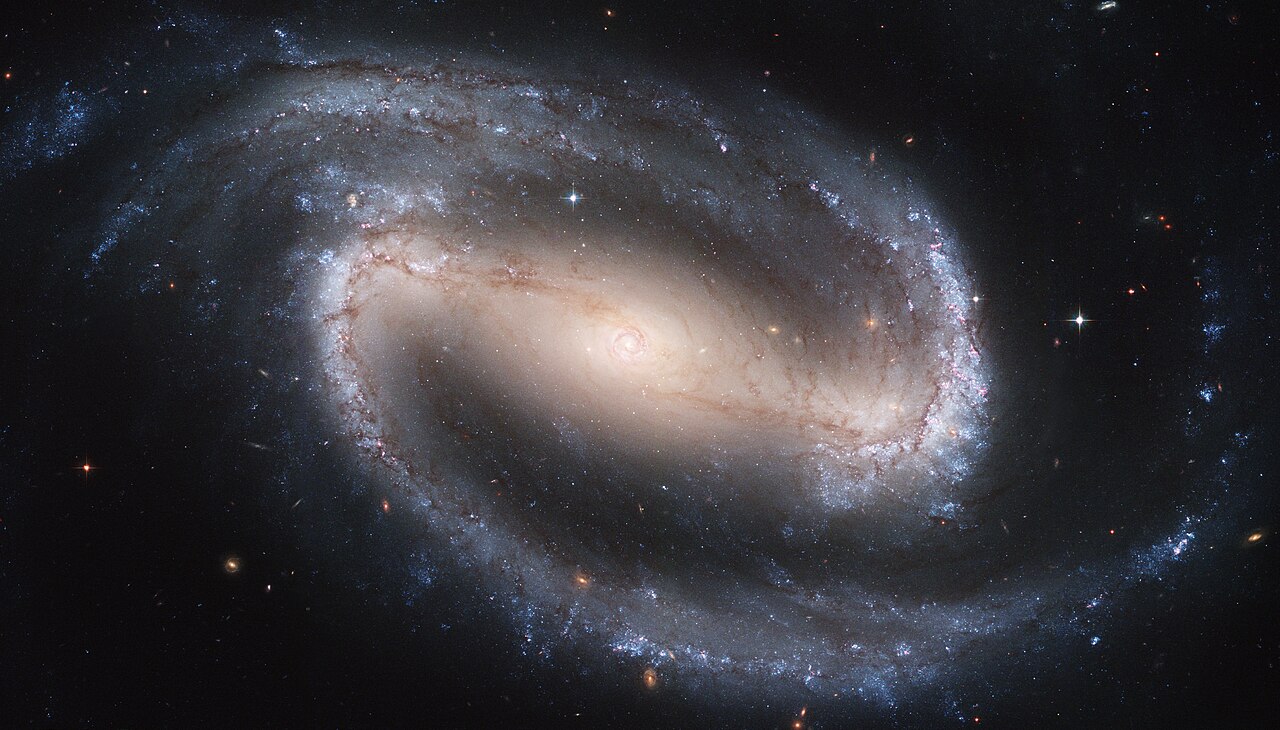
A speaking spiral galaxy called NGC1300 seen by Hubble. NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Legacy Team (STScI/AURA)/Wikimedia
The researchers were surprised
Based on research following observations from the James Webb Space Telescope, a talking Frisbee was found in some of these objects as early as 11 billion years ago, according to Science Alert. The universe today.
This suggests that they evolved faster in the early universe than previously expected.
Our home, the Milky Way, is a spiral galaxy with spiral arms radiating from its central core. Our solar system is located about 25,000 light-years from the center.
However, if you look at the rest in the sky, it is difficult to decide which one might be which type, but they generally fall into four main categories.
Edwin Hubble attempted to give some structure to the different shapes by developing a classification system that distinguished not only shape but also subclasses within galaxies.
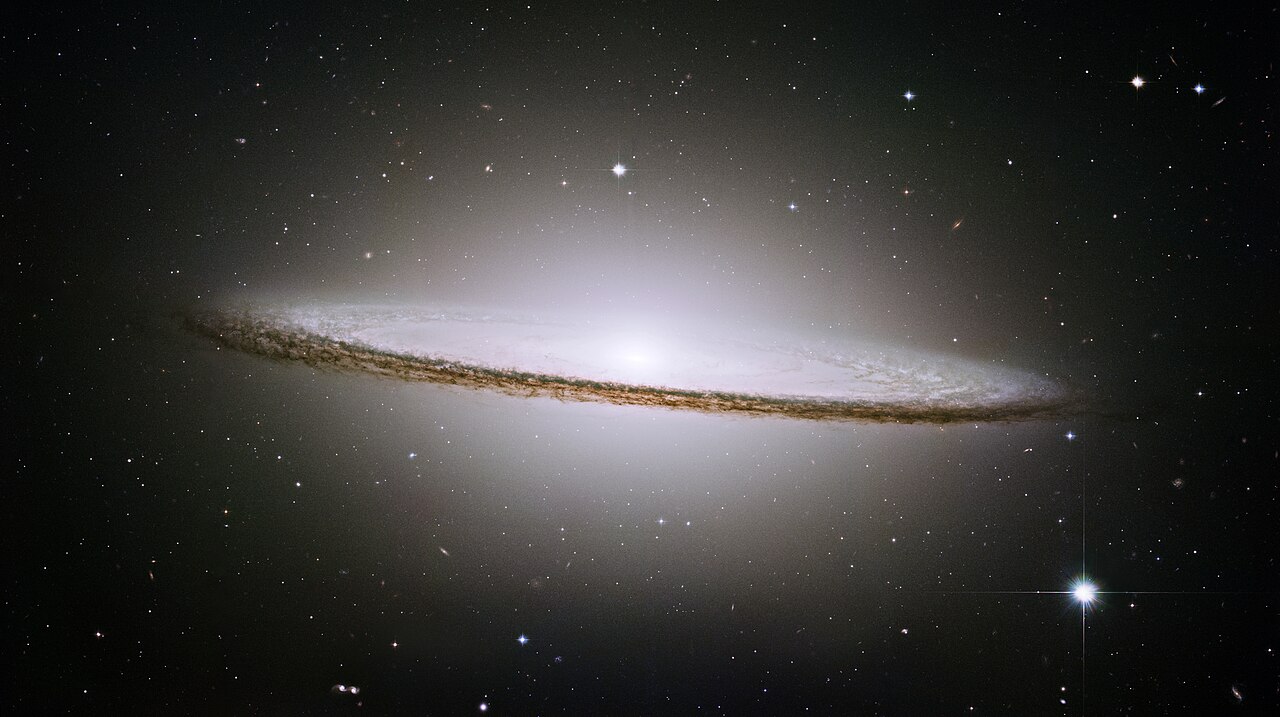

Although Messier 104, or the Sombrero Galaxy, appears ideal, it is currently unclear which category it falls into. NASA/ESA and Hubble Legacy Team (STScI/AURA)/Wikimedia
It has been known for a long time that these objects are not static, because they are constantly moving, changing and transforming.
In spiral galaxies, for example, spokes form as they become old. These connect spiral arms rather than a core, and are thought to form temporarily when accretion of gas triggers an explosion of star formation.
The presence of a beam in a spiral galaxy indicates that the object is completely stable. Understanding speech formation is key to understanding the evolutionary processes that occur there.
All previous observations have shown that the speaker's appearance decreases significantly from the near-entropy to redshifts close to one. This indicates that the speaker appeared to be a modern feature and was not present in the early universe.
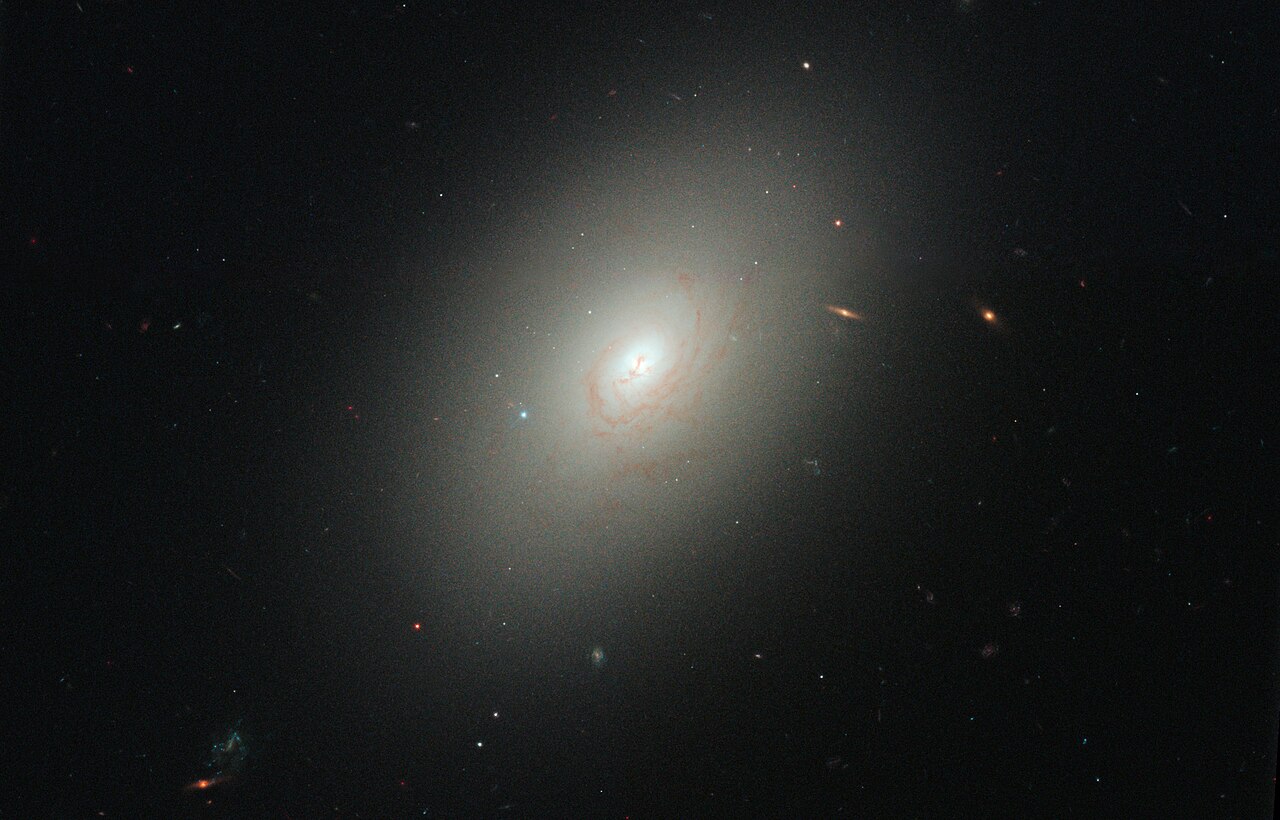

The elliptical galaxy named NGC 4150. NASA, European Space Agency, et al./Wikimedia
Isn't the speaker just describing ancient galaxies?
In the new study, specific features of higher redshift phenomena are being studied, lead author Zoe A Le Conte described.
However, only those included in the Deep Near Infrared Cosmic Survey of Extragalactic Legacy were sampled, so the sample consists of 368 objects.
The study showed that Webb's infrared sensitivity detected twice as many talking galaxies as Hubble's more blue-sensitive imaging platform.
According to the work of Le Conte and his team, spoke formation in such objects began much earlier, about 11 billion years ago.
Worth reading: