Located in the Bahamas, newly set marine green belt It is estimated to cover 92,000 square kilometers, the size of the US state of Maine, and possibly one of the largest marine carbon sinks in the world, according to the Nature Communicationss was published in a trade magazine on tuesday study authors.
Universe oceans – particularly seagrass ecosystems – in many areas They are poorly plannedmainly because it is difficult to measure with remote sensors such as satellites, writes A Bloomberg.
From space, marine prairies can easily be confused with phytoplankton, algae, or sediments.
This seaweed can play an important role in Climate emergency In slowing down while the world a coal different from the atmosphere Develops strategies. According to the lead scientist on the study, this discovery could give hope for the future of our oceans.
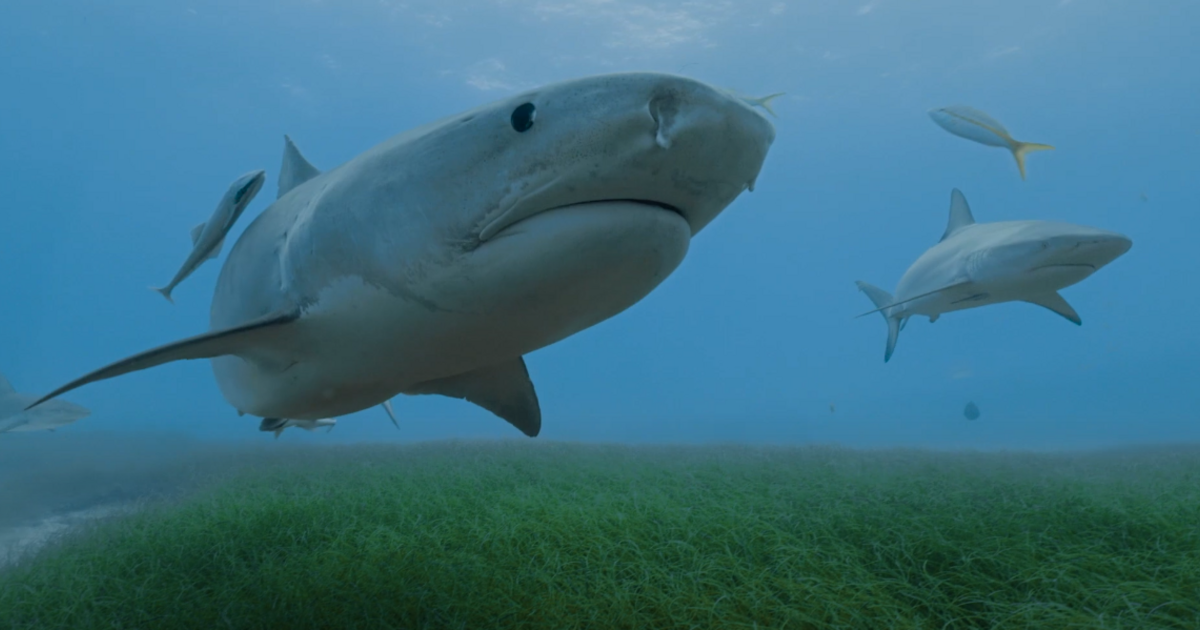
The largest marine predator helps map the extent of kelp
To conduct the research, the authors took an innovative approach and brought together scientists, divers, environmentalists, local stakeholders, and tiger sharks, the largest marine predator found in tropical seas.
Researchers soon realized that sharks had advantages over satellites and humans.
Tiger sharks spend about 72 percent of their time patrolling the seagrass beds, which can be observed using the 360-degree cameras we’ve installed on sharks for the first time.
said one of the study authors.
Tiger sharks travel about 70 kilometers in a single day, and are able to assist in the search 24 hours a day. Its great advantage is that it is not limited, like human divers, to shallow depths.
The newly mapped area spans between 66,000 and 92,000 square kilometres, a 34 percent increase in the area of seagrass documented worldwide over current estimates.