Everything is connected to everything – we can often hear this phrase in a different light, but perhaps no one believes that the harmful effects of climate change can cause a serious problem thousands of kilometers away from a certain place – so extreme weather events such as forest fires and floods In fact they can be related. But no one should have any doubt.
Connected weather events are called telecommunications, that is, communication between weather in distant regions of the Earth. These show how climate events occurring in one part of the world affect and have an impact on the weather hundreds or thousands of kilometers away. It’s like a global domino effect
– explains Jingfang Fan, employee of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research.
To explore these relationships, researchers have developed a new method of climate network analysis that can greatly aid in understanding interconnected events. These grids are like maps, where data points represent locations and show similarities due to the relationship between them. Thanks to this method, many sensitive areas have already been successfully identified.
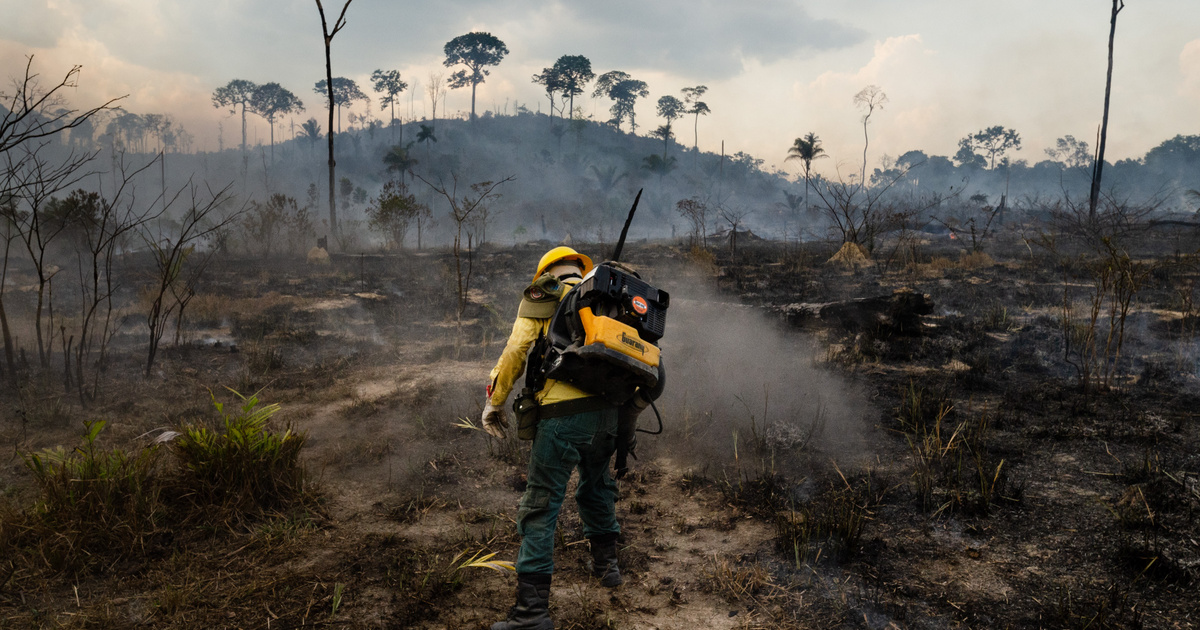
The Amazon fire also destroyed the Tibetan Plateau
Researchers were able to find the relationship between this sensitive area and the turning point half a year ago, because according to a study, climate change in the Amazon rainforest directly affects the Tibetan Plateau as well.
the In the journal Nature The published research revealed the relationship between the two areas at risk, but they are quite far from each other. The study discovered a potential domino effect between so-called tipping points, such that once one of these points falls, it significantly affects other regions of the world – for example, forest fires in the Amazon could cause problems in Tibet.
The publication supports the existence of so-called teleconnection, that is, the fact that climate change can have continuous effects that can be felt thousands of kilometers away.
It has been shown that extreme climate events are synchronized between the Amazon region and the Tibetan Plateau. The Amazon is a hugely important turning point due to its incredible size, and is also largely responsible for the planet’s carbon dioxide and water cycles. In addition, a quarter of the world’s species live here, but this has been decreasing significantly since the beginning of the 2000s.
So the researchers mapped temperature changes in more than 65,000 regions of the world over the past 40 years, allowing the study authors to identify interconnected changes between regions. Computer models then simulated possible outcomes in the two connected areas, and the results were far from good.
For example, as the amount of rain in the Amazon rainforest began to increase, the amount of snow falling on the Tibetan Plateau began to decrease.
Thus, it is not surprising that when the temperature rises, for example, due to a forest fire in one, a similar rate of warming can be observed in the other. Data quantifying the extent of the snow cover shows that the Tibetan Plateau has been losing thickness every year since 2008. This could have serious consequences, because the Tibetan Plateau is a source of water for millions of people, but without the melting snow cover all this would disappear.