Have you ever wondered what is the farthest star that can be seen with the naked eye when scanning the night sky? If so, here is the answer.
the According to a space.com article We can see with the naked eye 9,000 stars looking up at the sky, which is an amazing number if we were to pick them apart and count them, yet it is only a small part of the universe.
The closest solar system that can be seen with the naked eye is Alpha Centauri, which is 4.25 light-years away from Earth. The closest star here is Proxima Centauri, but since it is a red dwarf its light is very faint, so it cannot be seen from Earth without a telescope.

Alpha Centauri A and B, the closest visible stars. Source: NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and Facebook
The farthest star visible to the naked eye is V762 Cas. It is located 16 thousand light years from Earth. It is 100,000 times brighter than our Sun, but its light has to travel a great distance to get here, so under ideal conditions we can only penetrate it with the naked eye looking up at the sky.
The light of the farthest star we can see with the naked eye is 2.5 million years old
By the way, every star that can be seen even without a telescope in the night sky is larger than our Sun. Solar stars, or even smaller, glowing balls of gas, are too faint to be seen even though they may be closer than their bright counterparts. It is worth noting that 9,000 stars are visible to the human eye and about a million invisible stars spread across the night sky.
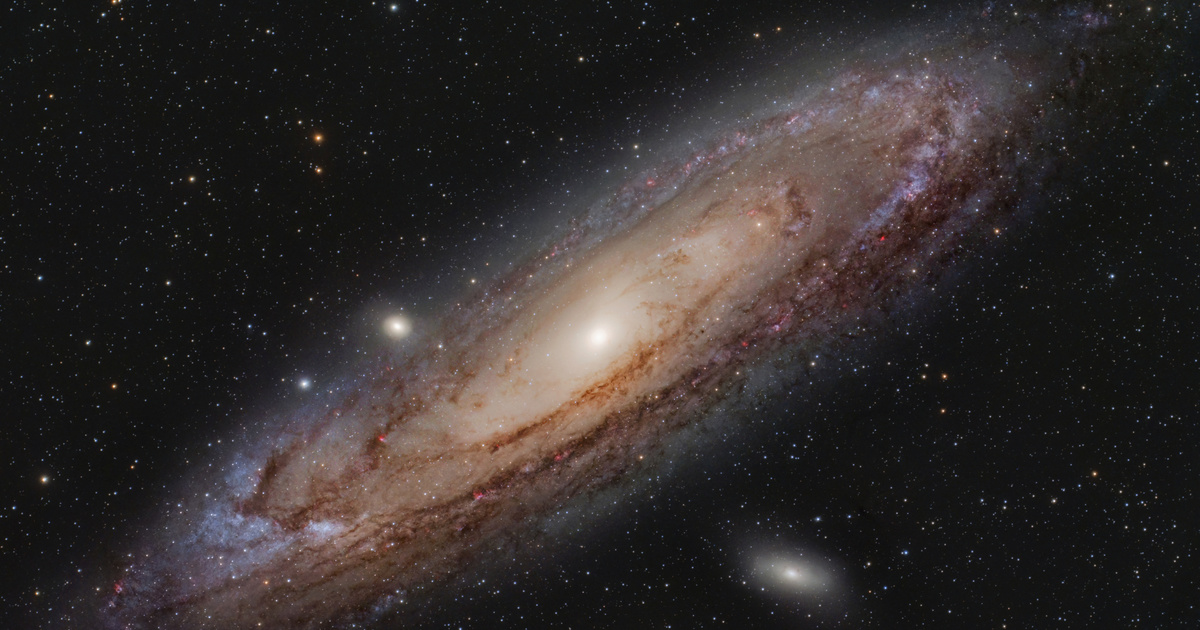
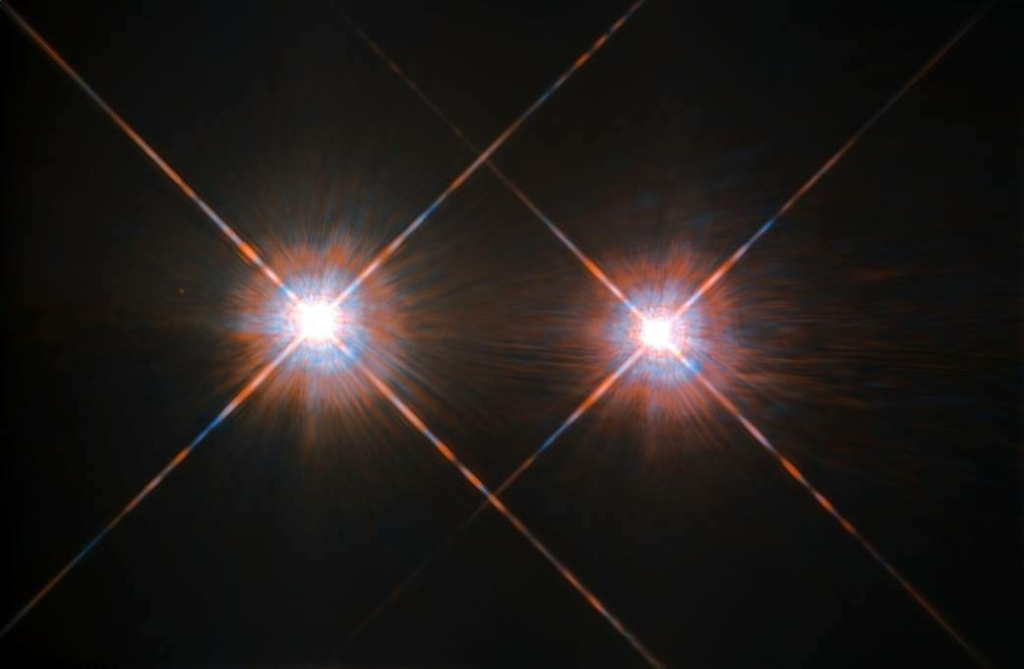
The farthest star we can see is V762 Cas, but it's not the farthest thing we can see with the naked eye from Earth. That is the Andromeda Galaxy, which contains a billion stars. From our planet, it looks like a dim dot about the size of our hand. If you look at the Andromeda Galaxy, you see the light that started there 2.5 million years ago.
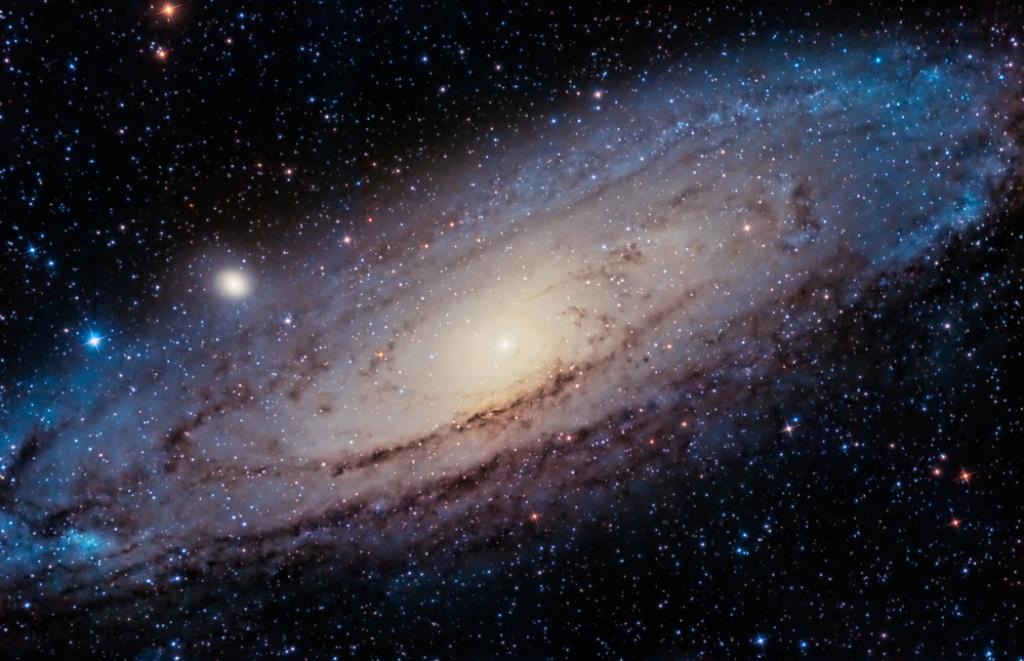

Andromeda Galaxy. Source: Depositphotos.com
We barely see anything from our galaxy
Meanwhile, there are solar flares and explosions that can make the star visible for a while. For example, a gamma-ray burst in 2008 made GRB 080319B visible for about 30 seconds. This star is located 7.5 billion light-years away. This means that when that light began its journey, the Earth did not even exist.
Interestingly, even with the most advanced telescopes, we cannot see 3% of the stars of the Milky Way, i.e. our galaxy, and we have not yet discovered 1% of galaxies.
The farthest star we've ever seen is Eärendel (yes from Lord of the Rings) which lies 28 billion light-years away, and formed 900 million years after the Big Bang, so it's a first-generation star. Its light was detectable to us for a short time due to gravity amplifying it. Using artificial gravity technology, it was possible to find JADES-GS-z13-0, which is located 33.6 billion light-years away and formed when the universe was only 400 million years old.
Here is Eärendel, the arrow shows:

Source: Facebook/Space News and Information
You may also be interested in:
- A terrible discovery related to Hungarian: many stars are planetary destroyers – read on here
- Life could thrive in a huge ocean of water on one of our solar system's Earth-like moons – details In this In our article
Opening image: Depositimages.com