On a historical geological scale, shortly after the appearance of unicellular eukaryotes, the multicellular organization of multicellular organisms began – They claim The Chinese researchers in their study published in the journal Science Advances on January 24.
Live sciences a description According to the study, well-preserved fossils of the tube-like Qingshania magnifica, classified as an ancient sperm algae, attest that 1.6 billion years ago, multicellular life flourished on the planet. The photosynthetic life forms composed of barrel-like cells unearthed from the Quanlingguo Formation in northern China are estimated to be 1.6 billion years old by researchers, who claim, based on spores in the samples, that the “primitive plants” investigated reproduced asexually. .
photo_camera
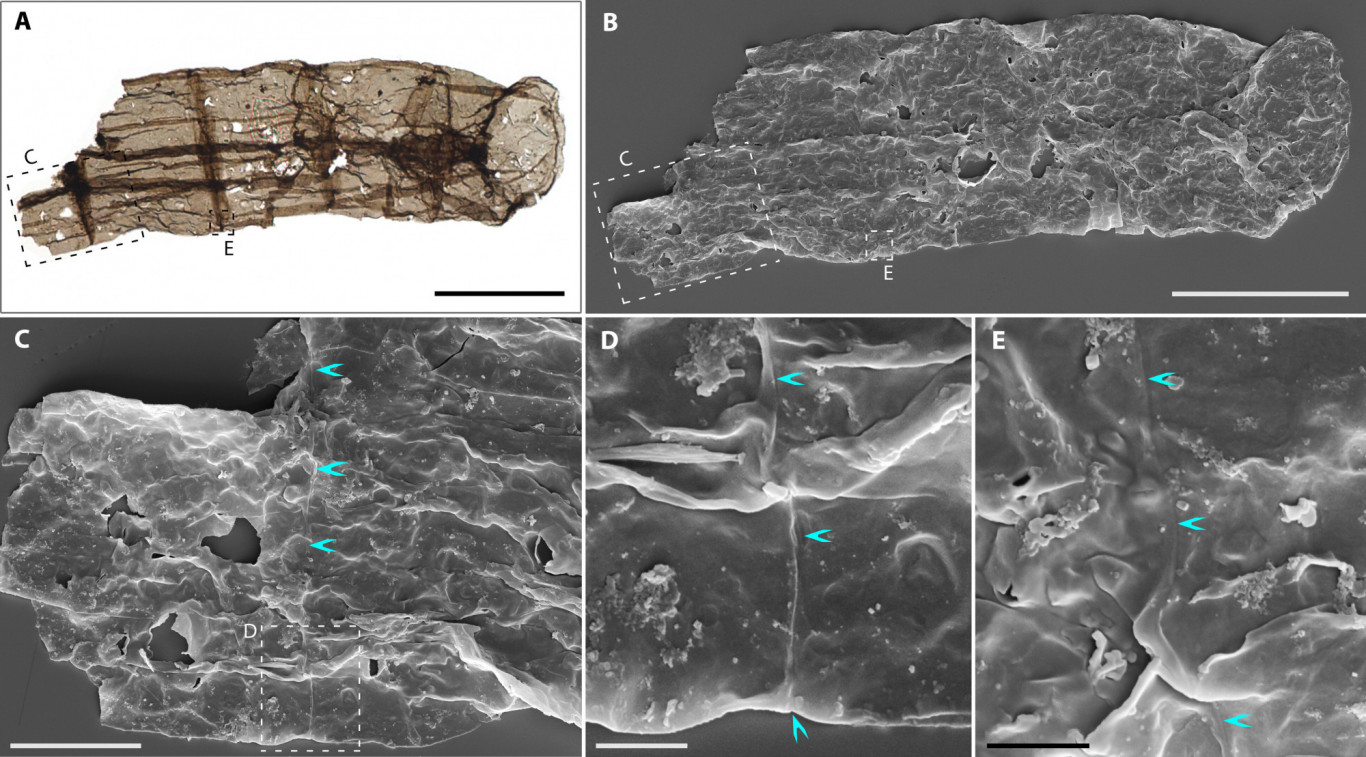
Fossil (A) and cell micrographs (B, C, D, E) of the ancient multicellular eukaryotic organism Qingshania magnifica
Image: Maoyan Zhu et al.
According to the current scientific situation, the first single-celled microscopic organisms without a nucleus, i.e. prokaryotes, appeared on Earth about 3.9 billion years ago, but the first single-celled eukaryotic organisms had to wait until 1.65 billion years ago. The Chinese researchers' findings show that multicellularity has been part of the lineage since the beginning of the evolution of eukaryotes.
the Kingshania magnifica The fossils have been known since 1989, but imaging techniques that allow a complete re-examination of the remains have only been available to researchers for the past few years – as stated in the description of the research.
Related articles about Qubit: