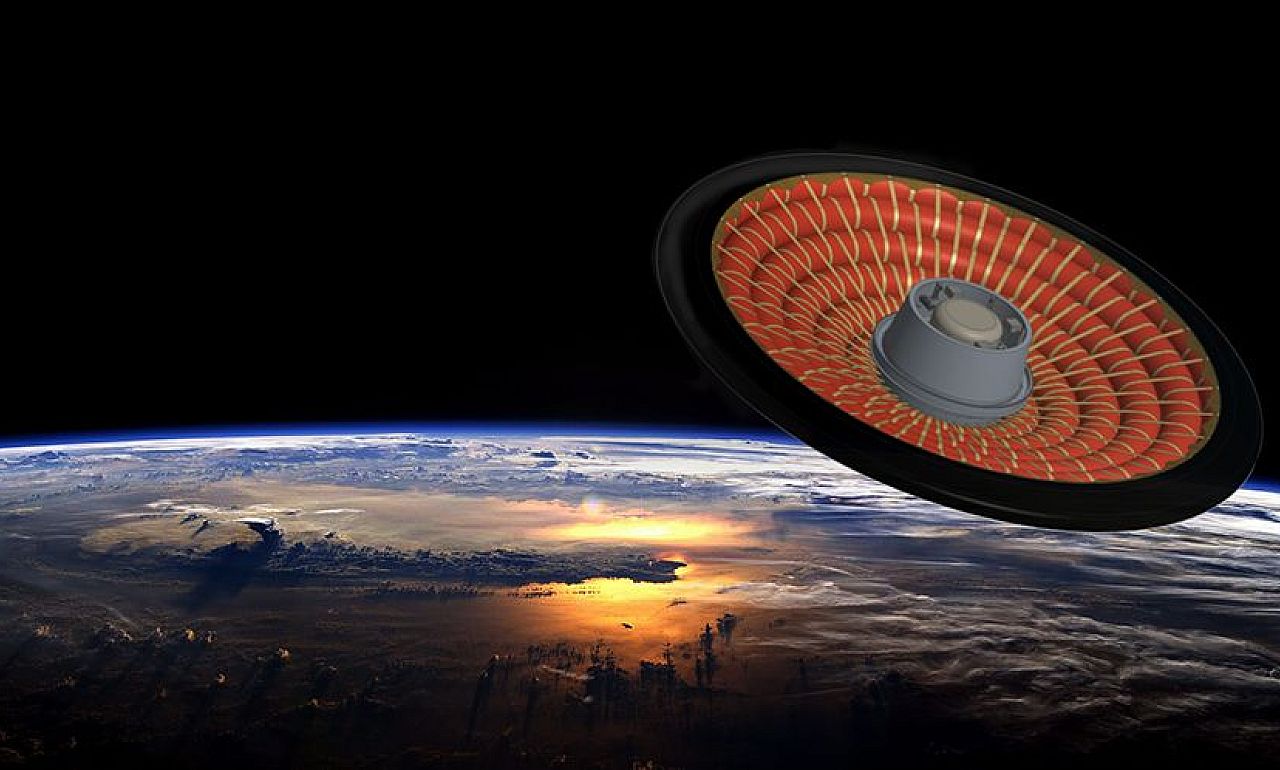
NASA today mentioned she was successful”blow decelerator(i.e. an “inflatable decelerator”) is the first test connected to spaceflight. The inflated structure, much like a saucer, will ensure the safe return of payloads from space to the Earth’s surface, in which case this has not been possible until now or at a very high cost .
For this, atmospheric braking force is traditionally used, which, however, has a big problem. That is, during deceleration, the kinetic energy of structures returning to Earth is converted into heat energy – and their environment becomes so hot that it has to be protected by heat shields against literal melting and burning.
At the same time, the size of the heat shields is limited by the size of the surface of the device itself – so they can only be effectively used for structures with a favorable mass / surface ratio. This is where the newly tested inflatable hysteresis shield comes into the picture, which can be scaled up to a size much larger than the space compartment, the rocket body or any other structure it would take into space with it and which would protect it from the heat during its return to Earth.
Moreover, the shield would be able to play a role also in the event of landing on other planets or moons with an atmosphere rarer than Earth’s, where a much larger braking shield would be required in the first place than when returning to Earth, in order to slow them down Enough for a safe landing at a low enough descent speed that it reaches close to the surface.