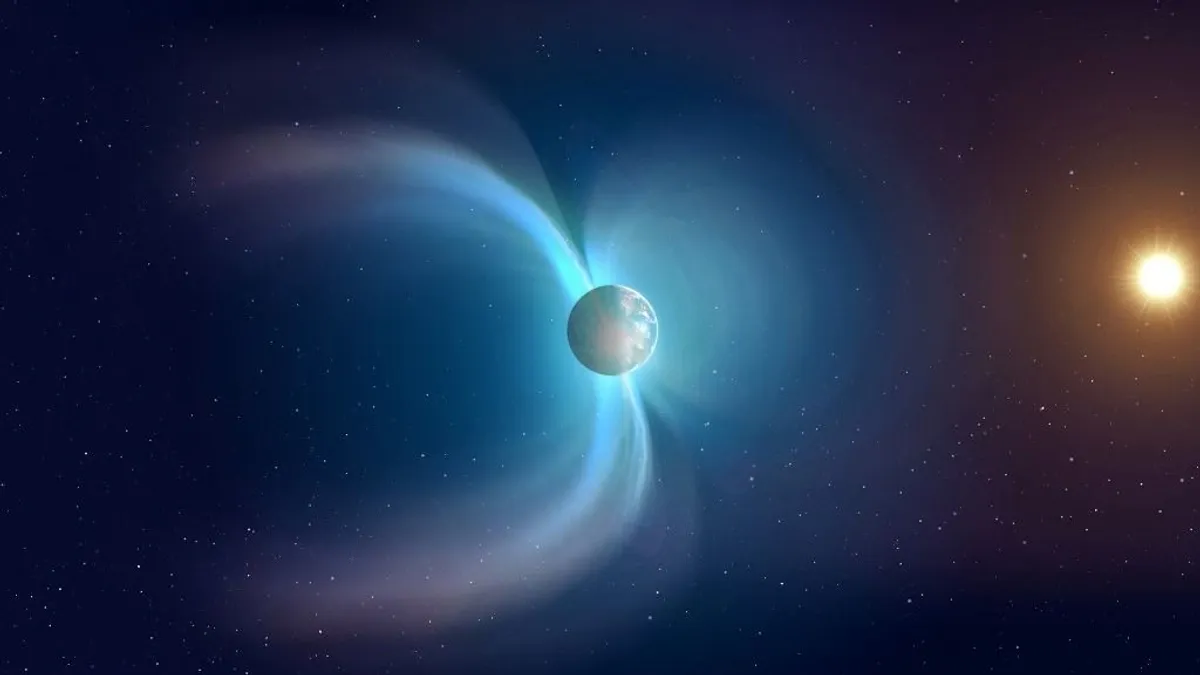
A Lachamp happened It is a shift in the Earth's magnetic pole resulting from the instability of the magnetic field resulting from liquid metals rotating in the Earth's core. The event was confirmed based on traces left in lava flows at Lachamp in France.
Image: Science Image Library via AFP
At the time of the event, the researchers showed that the field strength had decreased significantly – only 5% of the current magnetic field strength – allowing cosmic rays from the Sun to penetrate the planet's atmosphere to a much greater extent.
This intense radiation may have led to ozone layer depletion and changes in global climate conditions. In addition, researchers believe so
This event may have contributed to the extinction of ancient megafauna in Australia, as well as a change in human lifestyles, particularly in relation to the use of caves.
– Reads Science Alert In his article.
The polar shift during the Lachamp event occurred in about 250 years, and the magnetic field remained in this state for 440 years. At that time, the Earth's magnetic field was so weak that many harmful impacts hit the Earth from space.
The effect of magnetic pole reversal on the modern world
The European Space Agency (ESA) has been operating since 2013 Swarm missionwhich tracks changes in the Earth's magnetic field. By analyzing data from the Swarm satellites, scientists discovered a region known as the South Atlantic Anomaly, where the magnetic field is particularly weak.
This anomaly exposes satellites passing through it to increased radiation, which increases the possibility of another magnetic polar shift occurring soon.
Although current research suggests that the anomaly in the South Atlantic does not necessarily indicate an impending pole reversal, scientists continue to monitor fluctuations in the geomagnetic field. A significant weakening or reversal of the magnetic field would not only affect technological systems such as satellites and radio communications, but could also affect life on Earth.