Researchers from the University of Göttingen said on Monday that the Neanderthal had already scratched art samples into the bones.
Evidence for Neanderthal Aesthetic Sense
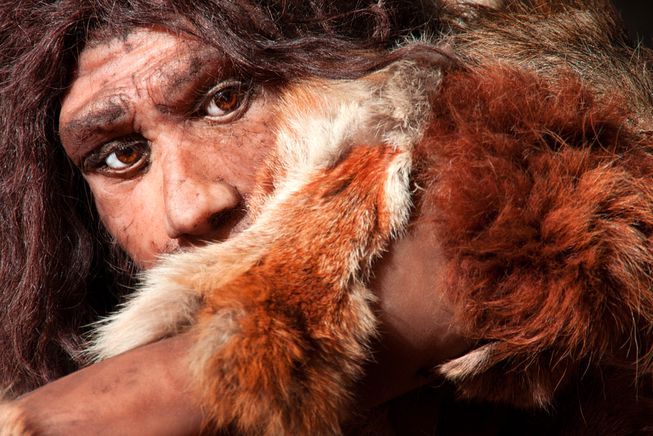
The patterns discovered on giant deer bones found in the Unicorn Cave in the Harz Mountains in Germany are exciting discoveries, suggesting that the genetically closest human ancestors have had amazing cognitive abilities for more than 50,000 years. Science has long considered Neanderthals to be relatively primitive, but this theory appears to be increasingly flipping.

Although it has long been known that Neanderthal tools and weapons were man-made,
But jewellery, cave paintings, and smaller figures have so far come almost exclusively from later times,
When modern humans (Homo sapiens) spread from Africa throughout Europe. An angled specimen of six rufts was engraved on one side of the hard toe bone that had just been found. A four-slit pattern appears at the bottom as well.

This discovery is evidence that neanderthals did indeed have an aesthetic sense
He was able to communicate through emoticons.
“This indicates the unique development of the creative ingenuity of Neanderthals,” said archaeologist Thomas Terberger. The new discovery was reported by the research team in the latest issue of the scientific journal Nature Ecology and Evolution.
Marks are engraved on the legs of an extinct giant deer
“It can’t be a coincidence that Neanderthals just chose an impressive antler bone for carving,” says Antje Schwalbe, a researcher at the Technical University of Braunschweig. The already extinct giant deer (Megaloceros giganteusThe horn grew up to four meters wide.

To date, only a few Neanderthal necklaces have been found and used as jewelry in France, as well as abstract motifs painted on cave walls in Spain. New discovery from Germany
One of the most complex forms of artistic expression to date devised by Neanderthals
London expert Silvia Bello writes. Researchers studying the discovery conducted experiments on the leg bones of deer today. It turns out that the bone must be cooked first so that only a stone tool can be used to carve a sample on the surface of the soft bone within an hour and a half.

The toe bone that holds the specimens alone is approximately six centimeters long, four centimeters wide, and three centimeters thick. It was discovered in 2020 at the entrance to the Unicorn Cave. Radiocarbon studies have found it to be more than 51,000 years old, much older than the 40,000-year-old motifs found in France. The latter is still debated as to whether it was an imitation of modern man’s art that had already reached Europe at that time.
(Source: MTI / dpa)