Although there is no shortage of complex questions about the universe, sometimes misconceptions need to be dispelled. Here is the answer to a question that people repeatedly ask on the Internet: “If there is no oxygen in space, how does the sun burn?”
First, there is very little molecular oxygen in space. It has been found in molecular form in a few places, including the Orion Nebula, the Rho Oviucci Cloud, and the Markarian Galaxy 231. Even in the Orion Nebula, there is little of it, and that is certainly not the reason why the Sun is “burning up.” Because it doesn't burn.
Earth is the only place in our solar system where we know fire exists. In fact, it is the only place in the universe, including stars. Where we know for sure that fire exists.
The sun is not a huge fireball
Fire requires free atmospheric oxygen. Without it, combustion simply does not occur, and for sustained combustion, experiments show that approximately 16 percent of the oxygen in the atmosphere is needed.
Despite being the third most abundant element in the universe after helium and hydrogen, free molecular oxygen is only found in abundance on Earth, where our atmosphere contains 21% oxygen.
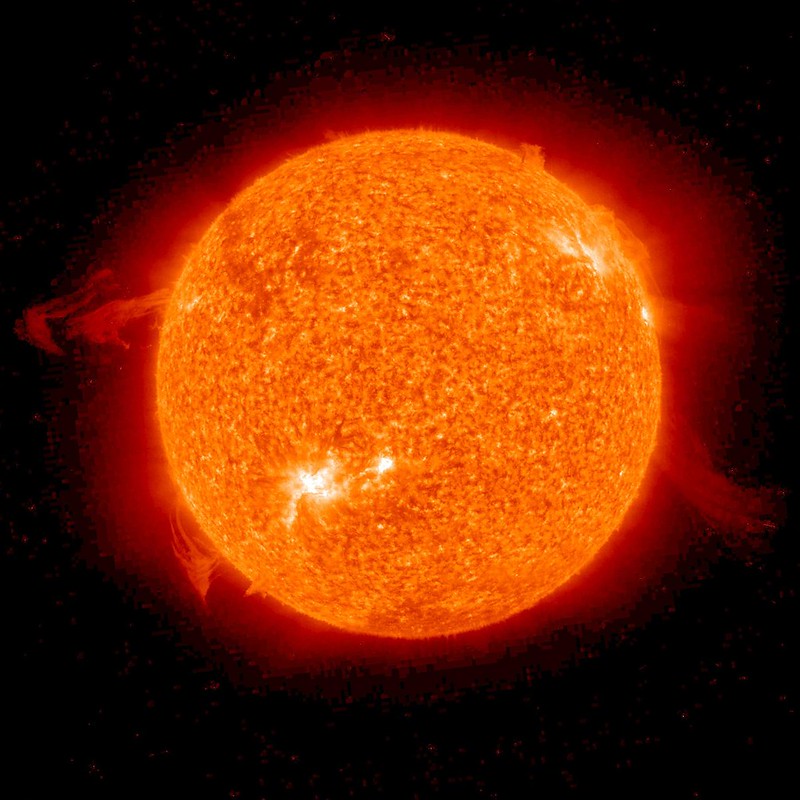
In terms of the number of atoms, the Sun consists of 91 percent hydrogen and 8.9 percent helium, and in terms of mass it consists of about 70.6 percent hydrogen and 27.4 percent helium. These ratios do not leave much room for the presence of oxygen, so maintaining fire is not possible. Instead, heat and light are created by nuclear fusion.
“The Sun's enormous mass is held together by gravity, creating enormous pressure and temperature in its core,” NASA explains.
The temperature in the core is about 15 million degrees Celsius, which is sufficient to sustain thermonuclear fusion. It is a process in which atoms combine to form larger atoms, releasing an incredible amount of energy in the process. In the Sun's core, hydrogen atoms fuse to form helium.
This produces the sun's heat and light. But if the sun does not burn and space is empty, how do we feel the heat of the sun on Earth?
Because there are fewer particles to interact with in the near-empty vacuum of space, there is not enough matter to heat it with radiation. The heat perceived on Earth is not direct thermal energy from the Sun, but is the result of the interaction of solar radiation emitted by the Sun (waves of the electromagnetic spectrum, including visible light) and particles on Earth.
Worth reading: